As the Internet of Things (IoT) moves from buzzword to widespread deployment, it has become clear that bandwidth, storage, latency, security, and other issues are serious limitations for many systems. This realization has resulted in the emergence of fog computing, a more distributed approach to data processing, analysis, and storage that delivers analytics when and where it’s needed.
Recognizing the need for this more distributed approach, Intel, ARM, Cisco, Dell, Microsoft, and the Princeton University Edge Laboratory formed the OpenFog Consortium in November 2015. The group’s goal is to define the fog computing architecture and ensure interoperability.
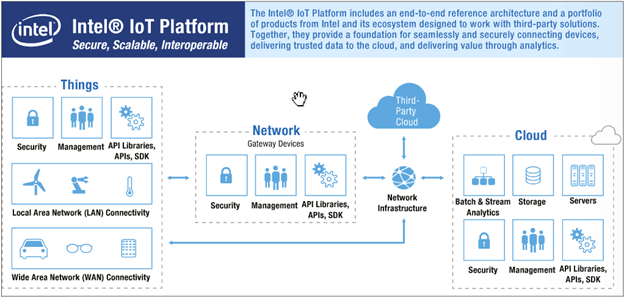
Already the group is finding common ground around the system architecture specification (SAS). This specification incorporates two aspects of the Intel® IoT Platform (Figure 1):
- Connecting “dumb” endpoints that lack integrated intelligence, security, and Internet connectivity
- Connecting smart devices and providing real-time, closed-loop control of data shared between the devices and the cloud
Figure 1. The Intel® IoT Platform is architected to enable a robust end-to-end IoT ecosystem. (Source: Intel.)
The Intel IoT Platform is an end-to-end reference architecture and portfolio of products from Intel and its ecosystem designed to work with third-party solutions. Together they provide a foundation for connecting devices, delivering trusted data to the cloud, and enabling analytics.
Timely analytics has been a key challenge for IoT deployments. For industrial control and manufacturing applications, latency requirements are often on the order of milliseconds—and missing this window can result in catastrophic failure.
The cloud isn’t well suited to real-time analytics in these scenarios. That’s why fog computing localizes data analysis where it can be most effective, transferring only metadata, exceptions, or extreme anomalies upstream. In doing so, latencies are reduced, but also less data is transferred back and forth to the cloud. This frees up bandwidth, helps lower overall power consumption, and enhances security.
How IoT Gateways Fill Out the Cloud
In many cases, the key to local analytics is the IoT gateway. Deploying a gateway with strong processing capabilities not only makes it possible to get various “things” connected, it also enables much of the analytics to happen where these things are located.
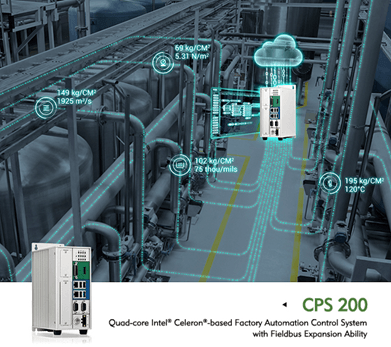
One good example is the Nexcom* CPS 200* (Figure 2), based on Intel® IoT Gateway Technology. Designed for ease of deployment and excellent security, the CPS 200 facilitates data acquisition and exchange among industrial control systems, and between factories and the cloud, paving the way for Industry 4.0.
Figure 2. The Nexcom CPS 200 is a powerful gateway.
A key feature of the CPS 200 is its quad-core Intel® Celeron® processor. This powerful processor lets the gateway go beyond basic data acquisition to perform robust analysis on the plant floor.
Another good example is the Dedicated Computing Edge7000 IoT Gateway (Figure 3). Like the Nexcom gateway, the Edge7000 IoT Gateway leverages an Intel Celeron processor to offer the performance needed to aggregate, verify, correlate, filter, and translate data at the edge. Another similarity is that both gateways are based on Intel IoT Gateway Technology, which provides a sophisticated, pre-integrated IoT software stack.
Figure 3. The Dedicated Computing Edge7000 IoT Gateway enables secure, seamless connectivity of a variety of devices.
The
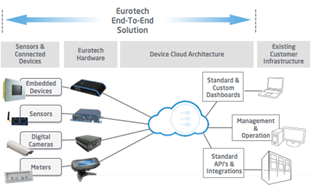
Eurotech ReliaGATE 20-25 also demonstrates the merits of edge intelligence. This powerful Intel® Atom™ processor E3800-based IoT gateway is designed for industrial and rugged applications. Eurotech uses the gateway to run its Everyware Software Framework (ESF) for application development, as well as its Everyware Device Cloud (EDC) M2M/IoT device integration platform (Figure 4).
Figure 4. The Eurotech Everyware Device Cloud enables end-to-end intelligence.
Rolling Out a Smarter IoT
These are just a few examples of the ways developers can implement fog computing. For more examples of IoT gateways—many designed for specific use cases—check out the Solutions Directory.